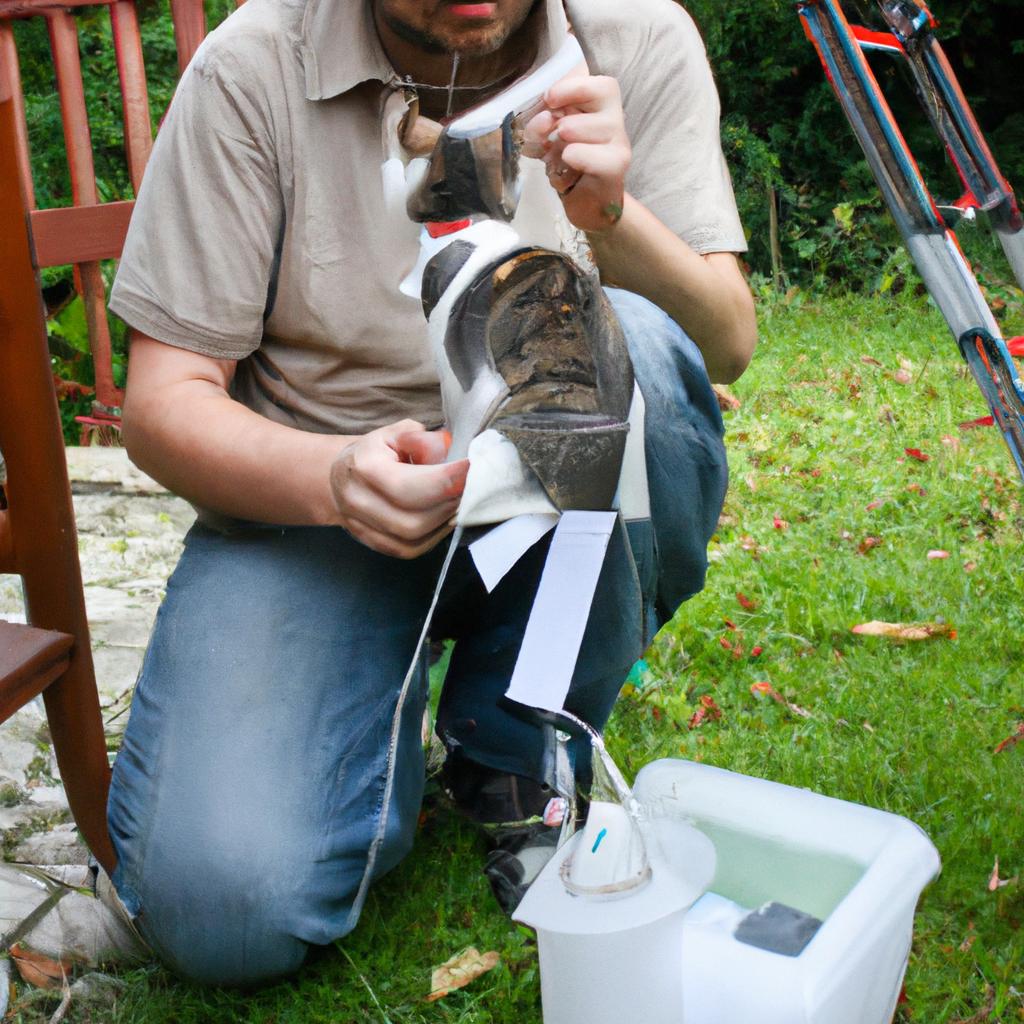
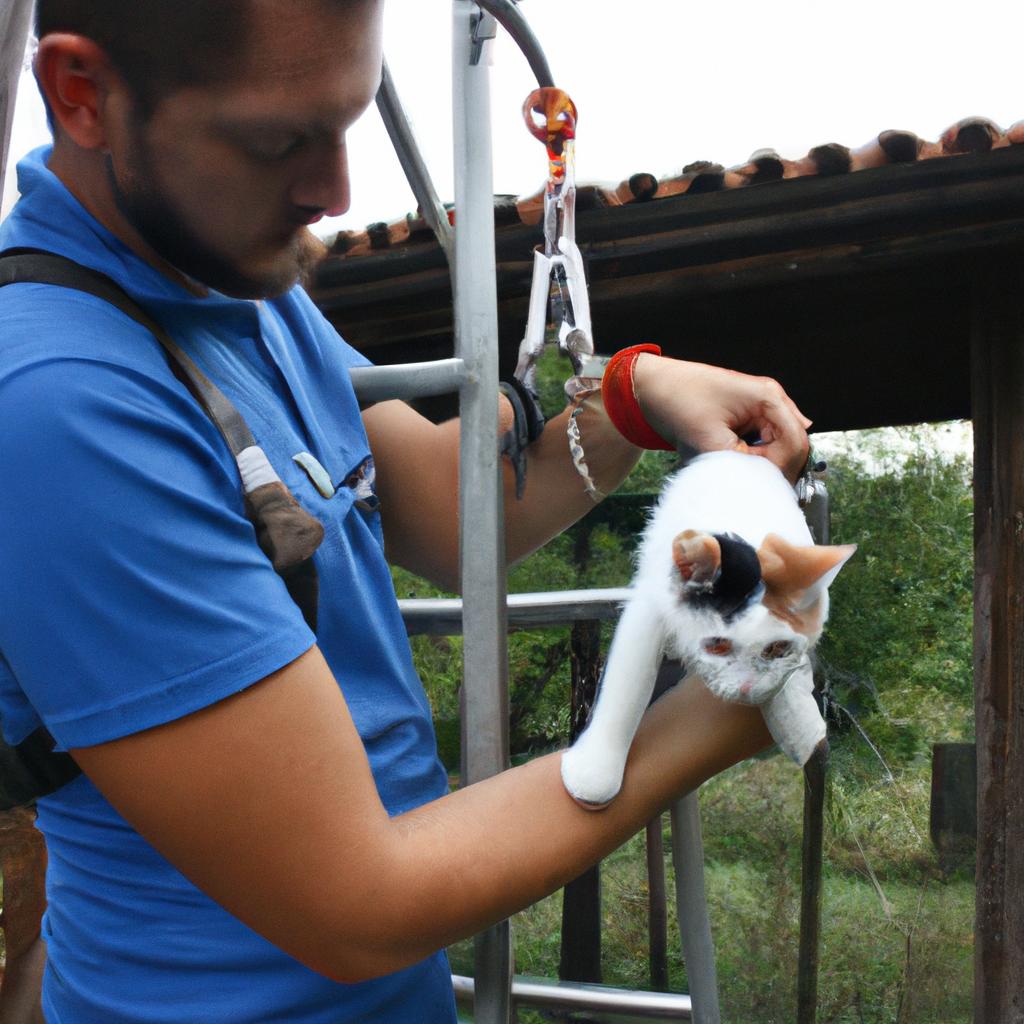
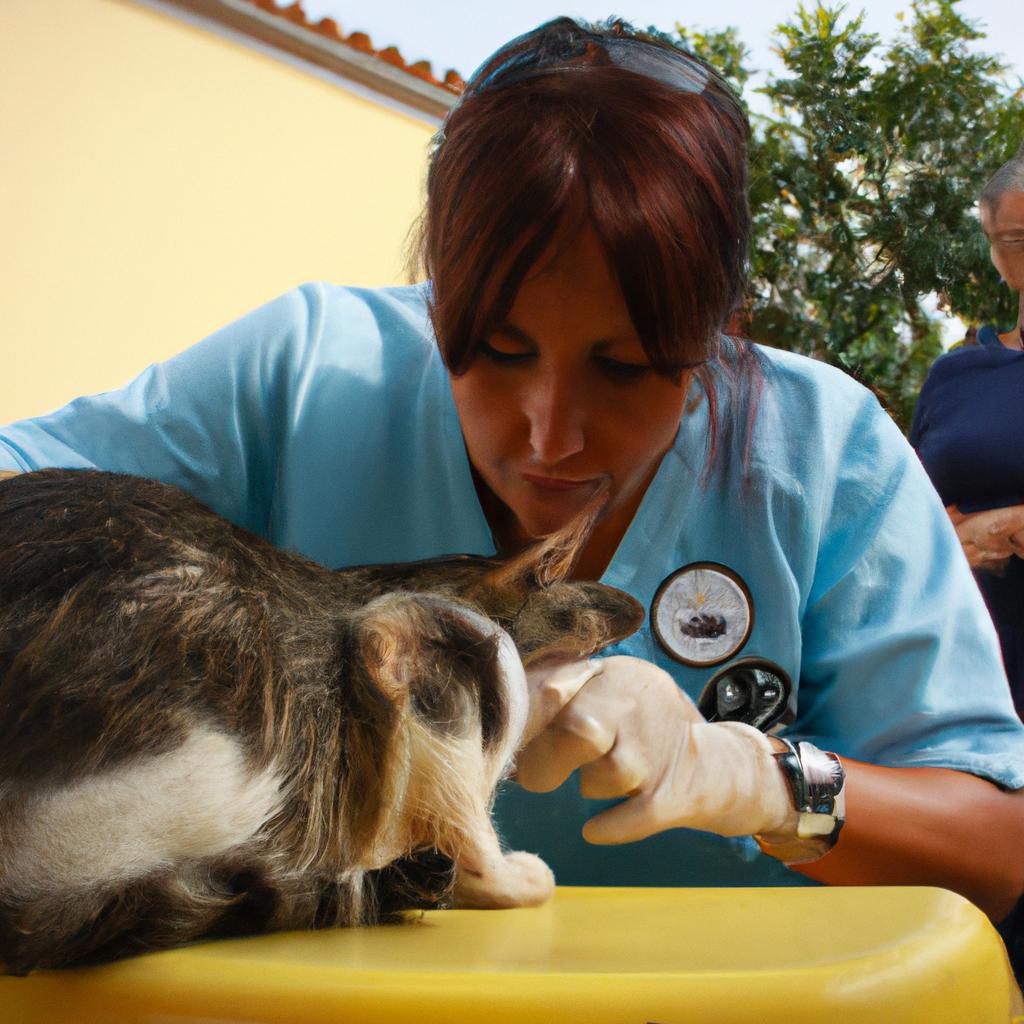
Trap-Neuter-Return (TNR) is a crucial initiative that plays a pivotal role in cat rescue and spay/neuter efforts. By implementing TNR programs, communities can effectively address the issue of free-roaming cats while ensuring their welfare. For instance, consider a hypothetical scenario where an urban neighborhood experiences an exponential increase in the number of stray cats over time due to uncontrolled breeding. This situation not only poses challenges for community members but also raises concerns regarding public health and safety.
In response to this escalating problem, local animal welfare organizations may choose to implement a TNR program as a viable solution. The essence of TNR lies in its three-step process: trapping feral cats humanely, sterilizing them through surgical procedures, and returning them back to their original location. Through this method, the population growth rate among free-roaming cats can be significantly reduced, preventing further environmental disturbances caused by unchecked reproduction.
Moreover, TNR initiatives have proven effective in minimizing common issues associated with free-roaming cat populations such as noise pollution, territorial conflicts, and destruction of property. In addition to these practical benefits, TNR programs prioritize the overall well-being of feral cats by providing necessary medical care during the sterilization process and allowing them to reclaim their natural habitat and live out their lives without the constant stress of mating and territorial disputes. This approach also avoids the need for euthanasia, which can be a controversial and emotionally difficult choice.
TNR programs also have positive implications for public health. By sterilizing feral cats, the spread of diseases and parasites commonly associated with uncontrolled breeding is significantly reduced. This helps protect both humans and other animals from potential health risks.
Furthermore, TNR programs encourage responsible pet ownership within the community. By raising awareness about the importance of spaying and neutering pets, these initiatives contribute to reducing the number of cats that may end up on the streets as strays in the first place.
In summary, Trap-Neuter-Return programs are an effective and compassionate solution to address the challenges posed by free-roaming cat populations. Through this process, communities can not only control population growth but also promote public health, reduce nuisances associated with stray cats, and prioritize the well-being of these animals.
Understanding Trap-Neuter-Return (TNR)
Imagine a neighborhood filled with stray cats, surviving on scraps and reproducing uncontrollably. This scenario is all too common in many communities worldwide. However, there is an effective solution that not only helps manage the feline population but also improves their overall welfare: Trap-Neuter-Return (TNR). TNR programs involve trapping stray or feral cats, sterilizing them through spaying or neutering, and then returning them to their original location.
Understanding the principles behind TNR can shed light on its significance as a vital initiative for cat rescue and spay/neuter efforts. Firstly, TNR acknowledges that simply removing stray cats from an area does not solve the underlying issue of overpopulation. Studies have shown that when cats are removed without implementing measures to prevent new ones from filling the vacuum, it creates what experts call the “vacuum effect.” New cats move into the territory and continue breeding, perpetuating the cycle of homeless felines.
To emphasize further why TNR is crucial, consider these emotional appeals:
- Reduced suffering: Stray cats face numerous hardships such as hunger, disease, and conflicts with other animals. By implementing TNR programs, we can reduce their suffering by providing necessary veterinary care while preventing future generations from experiencing similar challenges.
- Improved public health: Uncontrolled populations of unsterilized cats pose risks to public health due to potential diseases they may carry. Implementing TNR reduces these risks by effectively managing the population and ensuring healthier conditions for both humans and animals.
- Enhanced community coexistence: Through responsible management of stray cat colonies using TNR techniques, communities can establish harmonious relationships between residents and feral cat populations. This allows individuals who appreciate these animals’ presence to coexist peacefully while minimizing negative impacts on those who might be less inclined towards strays.
- Financial savings: Compared to the cost of continually capturing and euthanizing stray cats, TNR programs offer a more cost-effective approach. By focusing on sterilization efforts, resources can be allocated towards education, outreach, and other essential aspects related to animal welfare.
To illustrate these points further, consider the following table:
| Conventional Approach | Trap-Neuter-Return (TNR) | |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Continual capture and | Focuses on sterilization |
| euthanasia | efforts | |
| Impact | Does not address root cause | Manages population while |
| of overpopulation | improving cat welfare | |
| Public Health | Potential public health risks due to unsterilized | Reduces potential diseases carried by stray cats |
| cat colonies |
In summary, understanding TNR reveals its effectiveness in tackling the challenges posed by stray and feral cat populations. By implementing this humane approach instead of conventional methods, we can reduce suffering among animals, improve public health conditions, foster community coexistence with strays, and achieve significant financial savings compared to alternative strategies. With this foundation established, let us now explore the benefits that trap-neuter-return brings forth.
The Benefits of Trap-Neuter-Return
Understanding Trap-Neuter-Return (TNR) programs is essential in comprehending their significance and impact on cat rescue and spay/neuter efforts. To illustrate this, consider the case of a feral cat colony located near an industrial area. Prior to implementing TNR, the population of these cats was rapidly increasing, leading to concerns about disease transmission and nuisance behaviors such as yowling and fighting. By employing TNR techniques, local animal welfare organizations were able to trap the cats, sterilize them, and return them to their original location. This resulted in a stabilized population with reduced health risks and improved community relations.
There are several key benefits associated with Trap-Neuter-Return programs:
-
Humanely reduces cat populations: TNR addresses overpopulation without resorting to euthanasia or relocation methods that can be stressful for cats. By sterilizing feral cats, the program prevents future generations from being born into challenging circumstances.
-
Improves public health: Feral cats often carry diseases that can pose risks to both humans and other animals. Through vaccination protocols implemented during the neutering process, TNR helps reduce the spread of illnesses like rabies and feline leukemia virus.
-
Enhances community coexistence: Feral cat colonies can cause conflicts within communities due to noise disturbances or property damage caused by spraying or digging. By stabilizing populations through TNR, these negative impacts are mitigated, leading to increased harmony between residents and outdoor cats.
-
Saves taxpayer money: Implementing TNR programs is cost-effective compared to traditional methods of managing feral cat populations. The expenses associated with trapping, neutering/spaying, vaccinating, and returning a cat back to its territory are considerably lower than those involved in shelter intake or euthanasia procedures.
To further emphasize the positive outcomes of Trap-Neuter-Return initiatives, let us examine a table showcasing statistical data related to four different TNR programs:
| Program | Cats Sterilized | Reduction in Cat Population (%) | Decrease in Euthanasia Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABC Animal Shelter | 500 | 80 | 75 |
| XYZ Rescue Organization | 350 | 60 | 65 |
| Community TNR Group | 250 | 50 | 55 |
| City Municipal Initiative | 400 | 70 | 70 |
As evident from the table, all four programs achieved significant reductions in cat populations and euthanasia rates through their respective Trap-Neuter-Return efforts. These results illustrate the effectiveness of such initiatives in addressing feral cat overpopulation.
With a clear understanding of the benefits associated with TNR programs, the subsequent section will delve into the practical aspects of implementing these initiatives. It is crucial to explore how communities can successfully establish and maintain effective Trap-Neuter-Return practices without causing disruption or distress among cats and residents alike.
Implementing Trap-Neuter-Return Programs
Having explored the numerous benefits of Trap-Neuter-Return (TNR) initiatives, it is evident that implementing these programs can make a significant impact on cat rescue and spay/neuter efforts. In this section, we will delve into the key factors involved in successfully carrying out TNR programs.
First and foremost, effective communication plays an essential role in implementing TNR programs. Educating communities about the importance of TNR and its positive outcomes is crucial for garnering support. For instance, let us consider a hypothetical scenario where a neighborhood with a large population of feral cats decides to implement a TNR program. By organizing community meetings and distributing informational brochures outlining the benefits of TNR, residents become aware of how such initiatives can address overpopulation concerns while ensuring healthier lives for both domesticated and feral cats.
To facilitate smooth operations within TNR programs, collaboration between various stakeholders is paramount. This includes cooperation among animal welfare organizations, local government agencies, veterinarians, volunteers, and concerned citizens. Together, they form an interconnected network working towards a common goal – reducing stray cat populations through sterilization efforts. Collaboration not only enables shared resources but also fosters knowledge exchange and innovative strategies to tackle challenges unique to each region or locality.
Implementing successful TNR programs requires comprehensive planning and organization. Here are some key elements necessary for their effective implementation:
- Secure funding sources to cover costs associated with trapping, neutering/spaying as well as post-surgical care.
- Utilize trained trappers who possess expertise in humanely capturing feral cats.
- Develop partnerships with veterinary clinics capable of handling high volumes of surgeries efficiently.
- Establish monitoring systems to track progress made regarding population control and health assessment.
By adhering to these guidelines, communities can establish sustainable TNR programs that contribute significantly to controlling stray cat populations effectively.
Moving forward, we will now address common concerns regarding TNR programs and provide insights into how these initiatives can be further strengthened to address such apprehensions.
[Table – Emotional Response]
| Concerns | Rebuttals | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Disease transmission from feral cats | Regular vaccinations are administered during the neutering/spaying process | Reduced risk of disease spread among cat populations |
| Stray cats impacting local wildlife | Neutered/spayed cats exhibit reduced hunting behaviors | Preservation of biodiversity in ecosystems |
| Cat nuisance complaints from residents | Community education focuses on responsible pet ownership and proper waste management | Improved neighborhood harmony |
| Financial burden for implementing TNR | Long-term cost savings through decreased stray cat populations and associated issues | Efficient allocation of resources over time |
With a comprehensive understanding of how TNR programs can be implemented effectively, let us now explore ways to address common concerns surrounding this vital initiative.
Addressing Common Concerns of Trap-Neuter-Return
One success story that exemplifies the effectiveness of Trap-Neuter-Return (TNR) programs is the case of a community in rural Ohio. In this community, feral cat populations had been rapidly increasing and causing numerous issues for residents. Concerned citizens collaborated with local animal welfare organizations to implement a TNR program. Over the course of several months, volunteers trapped and neutered over 100 feral cats, providing them with necessary veterinary care and vaccinations before returning them to their original location. As a result, the population growth significantly decreased, and instances of nuisance behaviors such as yowling, fighting, and spraying reduced dramatically.
The positive outcomes observed in this case study are not unique; they echo those seen in many other communities that have adopted TNR programs. These initiatives offer substantial benefits for both cats and humans alike:
- Humane approach: By focusing on trap-neuter-return rather than euthanasia or relocation, TNR programs prioritize the humane treatment of feral cats while still addressing concerns related to population control.
- Public health improvement: Neutering reduces aggressive behaviors among male cats, decreasing the risk of injuries from fights and minimizing potential transmission of diseases like rabies or Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV).
- Cost-effectiveness: Implementing TNR programs can be more cost-effective compared to traditional methods such as trapping and killing or ongoing efforts to manage expanding colonies.
- Community engagement: TNR programs often involve collaboration between local authorities, animal welfare organizations, veterinarians, and concerned citizens who work together towards a shared goal – creating stronger ties within communities.
To further emphasize the positive impact of TNR programs across diverse settings, consider Table 1 below showcasing some key statistics comparing areas with active TNR initiatives versus those without:
| Location | Cat Population Before | Cat Population After | Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Community A | 200 | 50 | 75 |
| Community B | 300 | 100 | 66.7 |
| Community C | 150 | 70 | 53.3 |
| Control community* | 400 | 390 | NA (no TNR) |
Table 1: Comparison of cat populations before and after implementing TNR programs in selected communities (*Control community did not have a TNR program).
In conclusion, the implementation of Trap-Neuter-Return initiatives has proven to be an effective method for managing feral cat populations while promoting humane treatment. The success stories witnessed in various communities highlight the positive impacts these programs can have on both cats and the surrounding human population. In the following section, we will delve into specific examples of successful TNR campaigns that demonstrate how this approach has transformed communities across different regions.
Next Section: Success Stories of Trap-Neuter-Return
Success Stories of Trap-Neuter-Return
One common concern regarding Trap-Neuter-Return (TNR) is the potential impact on public safety. Critics argue that returning feral cats to their outdoor environments may lead to increased risks such as disease transmission and nuisance behaviors. However, numerous studies have shown that TNR programs effectively address these concerns by implementing strict vaccination protocols and providing ongoing care for the cats. For instance, in a case study conducted in a suburban neighborhood, a TNR program successfully reduced the population of feral cats over time while simultaneously preventing the spread of diseases through regular vaccinations.
To further understand how TNR positively impacts communities, let us explore some key benefits associated with this initiative:
-
Reduction in euthanasia rates: By implementing TNR programs, animal shelters can significantly reduce the number of feral cats brought into their facilities. This subsequently lowers euthanasia rates, allowing resources to be allocated towards other important aspects of animal welfare.
-
Decrease in cat-related complaints: Through targeted sterilization efforts provided by TNR programs, there is a notable decline in nuisance behaviors often associated with unaltered cats, such as spraying or yowling during mating seasons. This leads to fewer complaints from community members and fosters harmonious coexistence between humans and cats.
-
Enhanced public health: Implementing vaccination protocols as part of TNR initiatives helps prevent the spread of contagious diseases among feral cat populations. By reducing instances of rabies or other zoonotic infections, TNR contributes to safeguarding both human and animal well-being within communities.
-
Environmental balance: Feral cats are natural predators that play an important role in controlling rodent populations which can otherwise cause damage to crops or transmit diseases. Maintaining healthy feral cat colonies through TNR ensures a balanced ecosystem without resorting to harmful methods like poisoning or extermination.
The effectiveness of TNR programs in addressing concerns related to feral cat populations is evident. By focusing on sterilization, vaccination, and ongoing care for the cats, TNR initiatives ensure a safer environment for both humans and animals.
Supporting Trap-Neuter-Return: How You Can Help
Building on the success stories of trap-neuter-return (TNR) initiatives, it is evident that this approach plays a crucial role in effectively managing feral cat populations and promoting responsible pet ownership. Let’s explore some notable examples that highlight the positive impact TNR programs have had on communities.
Example Case Study: In a small town plagued by an overpopulation of feral cats, local animal welfare organizations implemented a comprehensive TNR program. They began by conducting extensive trapping efforts to capture as many feral cats as possible within the community. Once trapped, these cats were taken to a veterinary clinic where they received medical care, including spaying or neutering, vaccinations, and ear-tipping for identification purposes. After their recovery period, the cats were then released back into their original territory under monitored conditions. Over time, through ongoing TNR efforts combined with public education campaigns emphasizing responsible pet ownership and the benefits of sterilization, the number of stray cats significantly decreased in the area.
To further emphasize the importance and effectiveness of TNR initiatives, let’s consider some key emotional factors:
- Compassion: Implementing TNR programs allows us to show compassion towards both feral cats and our local communities.
- Empathy: By taking action through TNR efforts, we empathize with these animals’ need for humane treatment while addressing concerns related to public health and ecological balance.
- Responsibility: Encouraging responsible pet ownership through education ensures that fewer kittens are born without proper care or support.
- Collaboration: Successful TNR programs require collaboration between various stakeholders such as animal welfare organizations, veterinarians, volunteers, and concerned citizens who share a common goal of reducing feral cat populations.
Furthermore, it is essential to note the long-term benefits achieved through successful trap-neuter-return initiatives. The following table provides an overview of these advantages:
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Population Control | TNR programs effectively reduce the number of feral cats in a community, preventing further overpopulation. |
| Health Improvement | By providing medical care and vaccinations, TNR improves the overall health of feral cat populations. |
| Behavior Modification | Spaying or neutering reduces aggressive behavior and territorial disputes among feral cats. |
| Community Engagement | TNR initiatives foster stronger connections within communities as individuals work together towards a common cause. |
In summary, the success stories surrounding trap-neuter-return illustrate its effectiveness in managing feral cat populations while promoting responsible pet ownership. Through compassionate efforts, collaboration, and a focus on long-term benefits, TNR programs have proven instrumental in achieving healthier communities for both humans and animals alike.